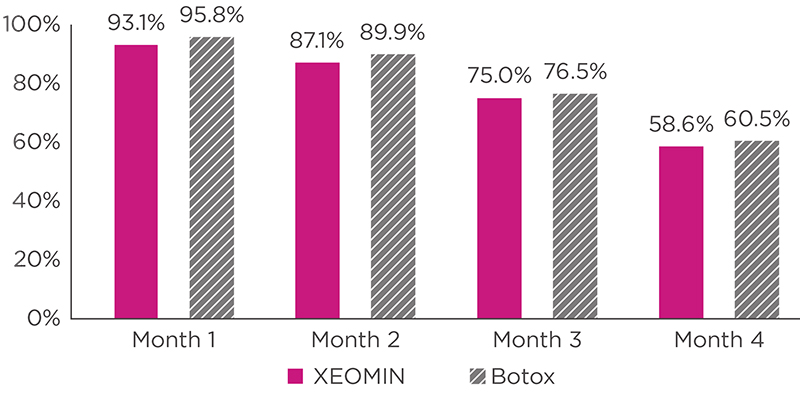
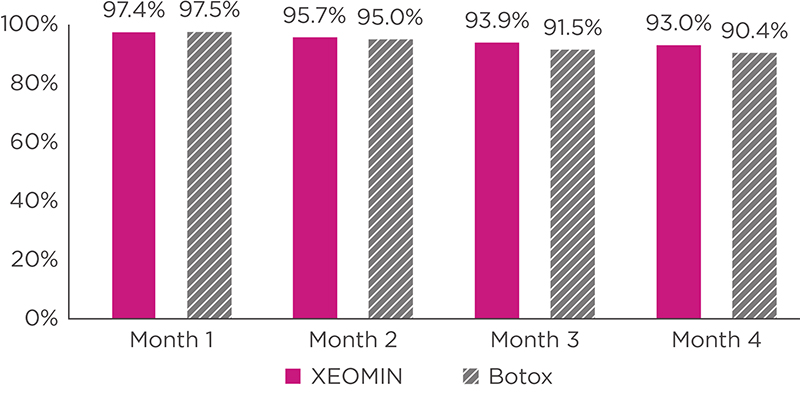
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
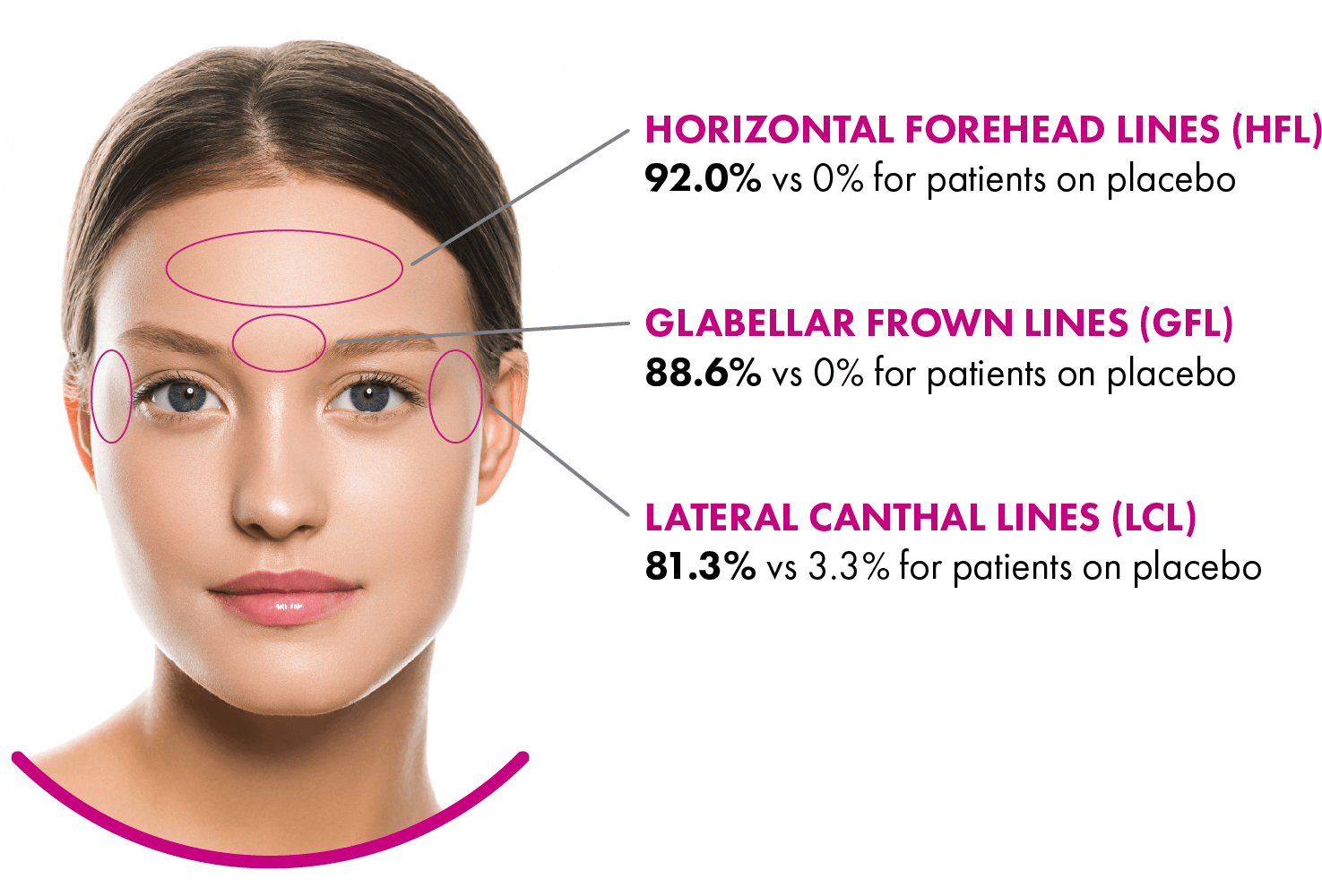
XEOMIN® (incobotulinumtoxinA) for injection, for intramuscular use is indicated for the temporary improvement in the appearance of moderate to severe upper facial lines in adults (glabellar lines with corrugator and/or procerus muscle activity [GL], horizontal forehead lines associated with frontalis muscle activity [HFL], and lateral canthal lines associated with orbicularis oculi activity [LCL].)
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: DISTANT SPREAD OF TOXIN EFFECT
See full prescribing information for complete BOXED WARNING.
The effects of XEOMIN and all botulinum toxin products may spread from the area of injection to produce symptoms consistent with botulinum toxin effects. These symptoms have been reported hours to weeks after injection. Swallowing and breathing difficulties can be life threatening and there have been reports of death. The risk of symptoms is probably greatest in children treated for spasticity but symptoms can also occur in adults, particularly in those patients who have underlying conditions that would predispose them to these symptoms.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with botulinum toxin products (anaphylaxis, serum sickness, urticaria, soft tissue edema, and dyspnea). If serious and/or immediate hypersensitivity reactions occur further injection of XEOMIN should be discontinued and appropriate medical therapy immediately instituted. XEOMIN is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any botulinum toxin preparation or to any of the components in the formulation.
Use in patients with an infection at the injection site could lead to severe local or disseminated infection. XEOMIN is contraindicated in the presence of infection at the proposed injection site(s).
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Treatment with XEOMIN and other botulinum toxin products can result in swallowing or breathing difficulties. Patients with pre-existing swallowing or breathing difficulties may be more susceptible to these complications. When distant effects occur, additional respiratory muscles may be involved. Patients may require immediate medical attention should they develop problems with swallowing, speech, or respiratory disorders. Dysphagia may persist for several months, which may require use of a feeding tube. Aspiration may result from severe dysphagia [See BOXED WARNING].
- The potency Units and Units of biological activity of XEOMIN are specific to their respective preparation and assay method utilized, and thus cannot be compared or converted into Units of any other botulinum toxin products.
- Individuals with peripheral motor neuropathic diseases, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or neuromuscular junctional disorders (e.g., myasthenia gravis or Lambert-Eaton syndrome) should be monitored particularly closely when given botulinum toxin. Patients with neuromuscular disorders may be at increased risk of clinically significant effects including severe dysphagia and respiratory compromise from typical doses of XEOMIN.
- Upper Facial Lines: Do not exceed the recommended dosage and frequency of administration of XEOMIN.
- GL: To reduce the complication of ptosis avoid injection near the levator palpebrae superioris, particularly in patients with larger brow depressor complexes. Corrugator injections should be placed at least 1 cm above the bony supraorbital ridge.
- HFL: Treat HFL in conjunction with GL to minimize the potential for brow ptosis.
- LCL: Avoid injections too close to the zygomaticus major muscle to prevent lip ptosis.
- Use caution when XEOMIN is used in patients who have marked facial asymmetry, with surgical alterations to the facial anatomy, pre-existing eyelid or eyebrow ptosis, when excessive weakness or atrophy is present in the target muscles, excessive dermatochalasis, deep dermal scarring, thick sebaceous skin (e.g., the inability to substantially lessen glabellar lines even by physically spreading them apart).
- Caution should be taken when XEOMIN is used where the targeted muscle shows excessive weakness or atrophy.
- XEOMIN contains human serum albumin. Based on effective donor screening and product manufacturing processes, it carries an extremely remote risk for transmission of viral diseases and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD). There is a theoretical risk for transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), but if that risk actually exists, the risk of transmission would also be considered extremely remote. No cases of transmission of viral diseases, CJD or vCJD have ever been reported for albumin.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Upper Facial Lines (Glabellar Lines, Horizontal Forehead Lines, and Lateral Canthal Lines): The most commonly observed adverse reaction (incidence ≥ 1% of patients and greater than placebo) for XEOMIN was injection site bruising (2%).
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Co-administration of XEOMIN and aminoglycoside or other agents interfering with neuromuscular transmission, (e.g., muscle relaxants), should only be performed with caution as these agents may potentiate the effect of the toxin.
Use of anticholinergic drugs after administration of XEOMIN may potentiate systemic anticholinergic effects. The effect of administering different botulinum toxin products at the same time or within several months of each other is unknown. Excessive neuromuscular weakness may be exacerbated by administration of another botulinum toxin prior to the resolution of the effects of a previously administered botulinum toxin.
USE IN PREGNANCY
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of XEOMIN in pregnant women. XEOMIN should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
PEDIATRIC USE
Safety and effectiveness of XEOMIN for upper facial lines in patients less than 18 years of age have not been established.
© 2024 Merz North America, Inc. All rights reserved. MERZ AESTHETICS and XEOMIN are registered trademarks of Merz Pharma GmbH & Co. KGaA in the U.S.